Glutathione - How It Works

The Science Behind Glutagem® Glutathione's Formulation
Glutathione is one of the body’s most powerful natural antioxidants — but it works best when supported by the right co-factors and nutrients.
That’s why Glutagem is more than just glutathione: it’s a carefully designed complex of synergistic ingredients that work together to improve absorption, recycling, and overall effectiveness. Here's how each ingredient contributes:
-
● L-Glutathione (Reduced) – The star of the formula, glutathione helps neutralise free radicals, reduce oxidative stress, and support melanin balance in the skin.
● NAC (N-Acetyl Cysteine) – A glutathione precursor that helps your body replenish glutathione naturally at the cellular level.
● Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA) – A universal antioxidant that regenerates both glutathione and vitamin C within the body, amplifying their effects. -
● L-Glutamine – An amino acid essential for tissue repair, immune support, and gut health — which is directly linked to skin clarity and inflammation control.
● Vitamin C – Crucial for glutathione regeneration and collagen production, it also supports skin brightness and barrier strength.
● Zinc – Plays a key role in skin healing, inflammation control, and melanin regulation, helping to minimise post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. -
● Selenium – Works with vitamin C and glutathione to combat oxidative damage at the cellular level and supports immune health.
● Biotin – Known for promoting healthy skin, hair, and nails, it also contributes to energy metabolism and cell renewal.
● Black Pepper Extract (95% Piperine) – Enhances bioavailability, helping your body absorb and utilise all active ingredients more effectively.
This combination is what sets Glutagem apart from basic glutathione supplements — it’s not just what you take, but what your body can actually use that makes the difference.

What is Glutathione?
Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant made naturally by the body. Often called the “master antioxidant”, it plays a vital role in protecting your cells, supporting detoxification, and maintaining healthy, radiant skin.
Glutathione is made from three amino acids:
-
Glutamine – supports tissue repair and gut health
-
Cysteine – provides sulphur, essential for detox pathways
-
Glycine – supports collagen, sleep, and liver function
Together, these form a tripeptide that your body uses to repair damage and neutralise toxins.
Your body produces glutathione in the liver, but it is also found in the skin, lungs, kidneys, and immune cells. You can also obtain it:
● In small amounts from foods like spinach, broccoli, and avocados.
● Through supplementation — Glutagem delivers 1000 mg of reduced L-glutathione, the most effective and bioavailable form.
What does glutathione do to your body and skin?
● Neutralises oxidative stress — protecting cells from free radical damage (a cause of dullness, wrinkles, and inflammation).
● Supports detoxification — helps the liver remove heavy metals, alcohol by-products, and environmental toxins.
● Promotes immune health — protects white blood cells and helps fight off illness.
● Regulates melanin production — which may help fade dark spots and support a clearer, more even skin tone over time.
● Boosts skin clarity and radiance — especially when combined with key nutrients like Vitamin C, NAC, and Selenium, as found in Glutagem.
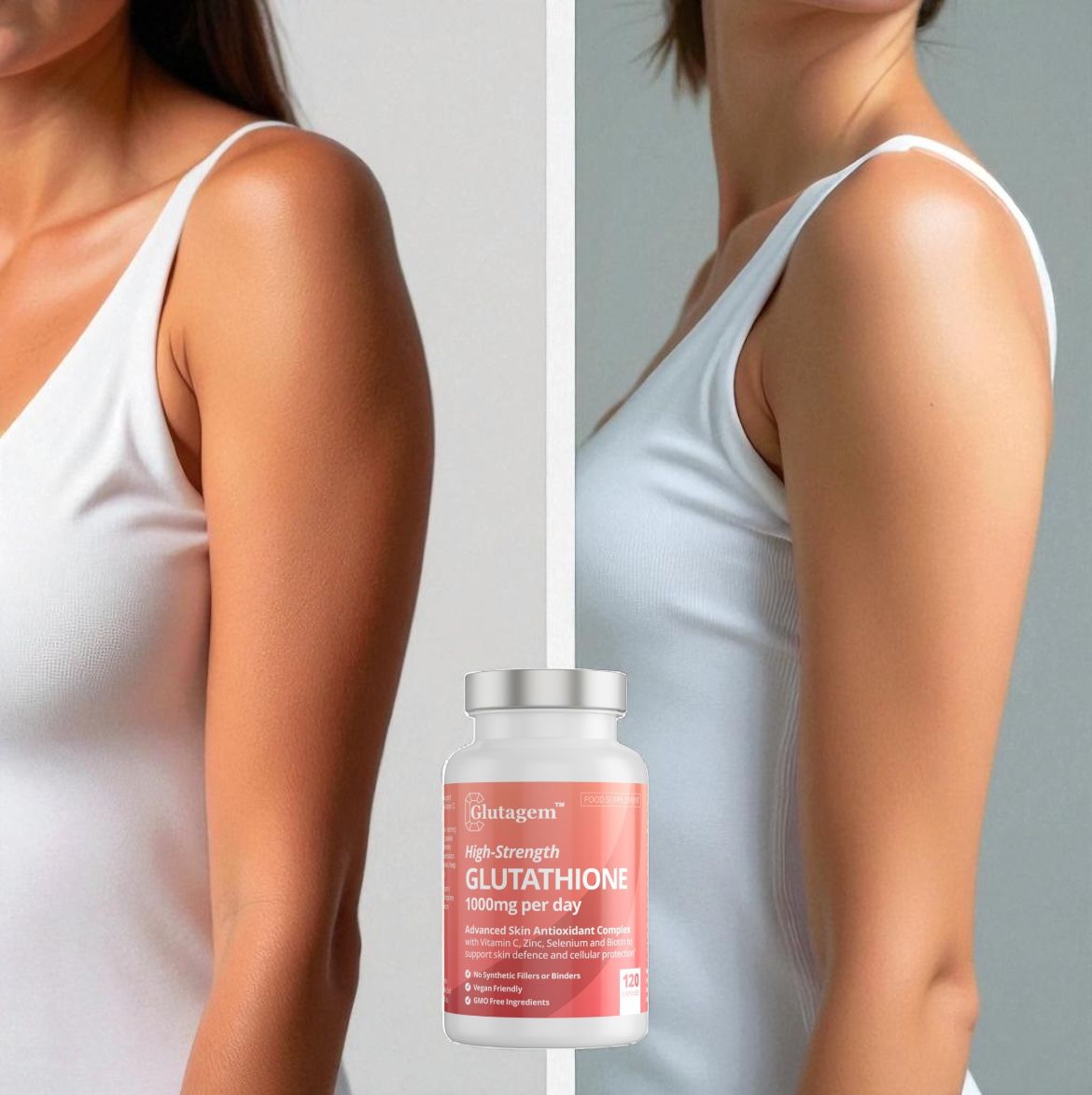

How Glutathione Supports Skin Brightening
Glutathione is widely recognised for its skin-brightening properties — not because it bleaches the skin, but because it works with your body’s natural systems to create a more even, radiant tone over time.
Here's how:
-
✔ Inhibits Tyrosinase – the Pigment-Producing Enzyme
Tyrosinase is the key enzyme responsible for converting tyrosine into melanin — the pigment that gives skin its colour.
Glutathione naturally inhibits tyrosinase activity, slowing down the overproduction of melanin that leads to dark spots, hyperpigmentation, and uneven tone. -
✔ Shifts Melanin production toward Pheomelanin
There are two main types of melanin in the skin:
● Eumelanin (dark brown/black pigment)
● Pheomelanin (light red/yellow pigment)
Glutathione influences the balance, encouraging your skin to produce more pheomelanin, resulting in a brighter, more luminous tone — especially in individuals with melanin-rich or unevenly pigmented skin. -
✔ Reduces Inflammation & Oxidative Stress
Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress (from sun exposure, pollution, or hormones) are major triggers for hyperpigmentation. As a master antioxidant, glutathione helps:
● Neutralise free radicals
● Reduce inflammatory responses
● Protect skin cells from UV-induced damage
This helps prevent the reactivation of pigmentation at its root cause. -
✔ Supports Liver Detox & Hormonal Balance
A sluggish liver or hormone imbalances (like oestrogen dominance or insulin resistance) can trigger melasma or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Glutathione plays a key role in Phase II liver detoxification, supporting the elimination of toxins and balancing the pathways that impact skin clarity.
-
✔ Visible Benefits Over Time
With consistent use, especially when paired with supportive nutrients like Vitamin C, Zinc, and Selenium, many users notice:
● Smoother, more even skin tone
● Fewer dark spots and pigmentation patches
● Brighter, healthier-looking skin
These results typically become more visible between 8 to 12 weeks, depending on your skin tone, lifestyle, and baseline pigmentation.
When Will I See Results?
Most users report visible improvements in skin tone, clarity, and brightness within 8–12 weeks after daily use. Consistency, hydration, and sun protection are key.

How to Use Glutagem
✔ Take 2 capsules in the morning and 2 capsules at night after meals.
✔ Maintain consistent use daily for best results.
✔ Pair with SPF and a quality skincare routine for faster impact.
✔ Glutagem works deep within your body to help reveal the glow you deserve.
Science & References
1. Glutathione inhibits tyrosinase and reduces melanin content
Nagapan, T.S., et al. (2019) ‘Oral supplementation of L‑glutathione prevents ultraviolet‑induced melanogenesis activity in mice’, Journal of Photochemistry & Photobiology B: Biology, [online]. Demonstrated that oral L‑glutathione significantly reduced both melanin content and tyrosinase activity in UVB‑irradiated mice, supporting its anti‑melanogenic effect.
2. Glutathione shifts melanin synthesis from eumelanin to pheomelanin
Sharma, D.K. & Sharma, P. (2022) ‘Augmented glutathione absorption from oral mucosa and its effect on skin pigmentation’, Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, [online]. Explains how glutathione influences melanogenesis by shifting the balance from darker eumelanin to lighter pheomelanin via inhibition of tyrosinase (by copper chelation and antioxidant effect).
3. Glutathione as a modality to modulate eumelanin/pheomelanin production
Singh, I.K., et al. (2024) ‘A review of therapies for hyperpigmentation modulating the synthesis of eumelanin to pheomelanin’, Archives of Dermatological Research, [online]. Highlights glutathione among several agents that can shift melanogenesis toward pheomelanin synthesis, offering insight into alternative hyperpigmentation therapies.
4. Glutathione derivatives and their anti‑melanogenic effects
Chung, B.Y., et al. (2016) ‘The glutathione derivative GSH‑monoethyl ester may enhance pheomelanin formation’, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, [online]. Investigated various glutathione derivatives in vitro and found that certain forms (e.g., GSH‑MEE) effectively reduce melanin and tyrosinase activity, increasing the pheomelanin/eumelanin ratio.
5. Mechanistic insight from broader reviews of antioxidant systems
Lu, Y., et al. (2021) ‘Modulating skin colour: role of the thioredoxin and glutathione systems’, Antioxidants, [online]. Reviews the antioxidant roles of glutathione and its interaction with thioredoxin pathways in skin cellular protection and pigmentation.
Online References
1.1. Dpcj.org. (2024). Glutathione for skin lightning: A regnant myth or evidence-based verity | Dermatology Practical & Conceptual. [online] Available at: https://dpcj.org/index.php/dpc/article/view/dermatol-pract-concept-articleid-dp0801a04/174?utm_source=chatgpt.com [Accessed 30 Aug. 2025].
1.2. Nagapan, T.S., Lim, W.N., Basri, D.F. and Ghazali, A.R. (2019). Oral supplementation of L-glutathione prevents ultraviolet B-induced melanogenesis and oxidative stress in BALB/c mice. Experimental Animals, 68(4), pp.541–548. doi: https://doi.org/10.1538/expanim.19-0017.
2. Sharma, D.K. and Sharma, P. (2022). Augmented Glutathione Absorption from Oral Mucosa and its Effect on Skin Pigmentation: A Clinical Review. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, Volume 15, pp.1853–1862. doi: https://doi.org/10.2147/ccid.s378470.
3. Singh, I.K., Espinosa, M.L., Lim, H.W. and Mohammad, T.F. (2024). A review of therapies for hyperpigmentation modulating the synthesis of eumelanin to pheomelanin. Archives of dermatological research.., [online] 316(9), p.668. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-024-03411-4.
4. Chung, B., Choi, S., Moon, I., Park, C., Kim, Y.-H. and Chang, S. (2016). The Glutathione Derivative, GSH Monoethyl Ester, May Effectively Whiten Skin but GSH Does Not. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(5), p.629. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050629.
5. Lu, Y., Tonissen, K.F. and Di Trapani, G. (2021). Modulating skin colour: role of the thioredoxin and glutathione systems in regulating melanogenesis. Bioscience Reports, [online] 41(5), p.BSR20210427. doi: https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20210427.


